[This article has been updated, original publish date: September 25, 2023]
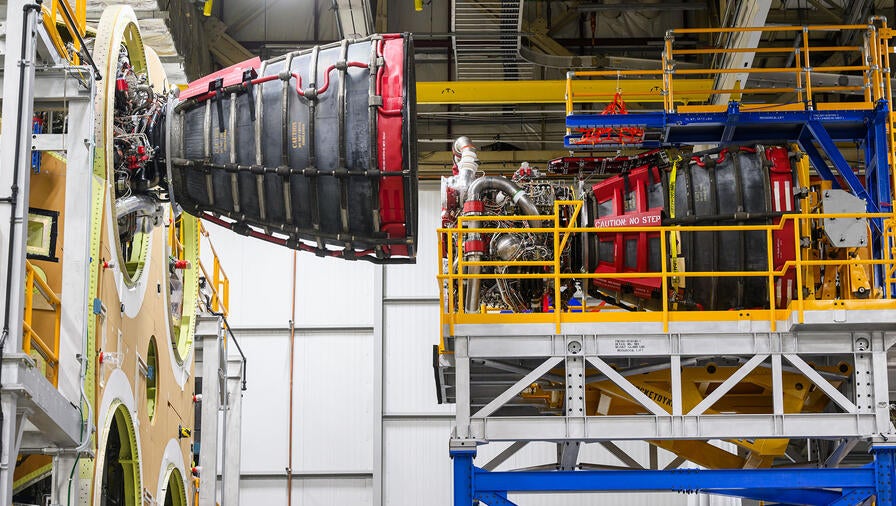
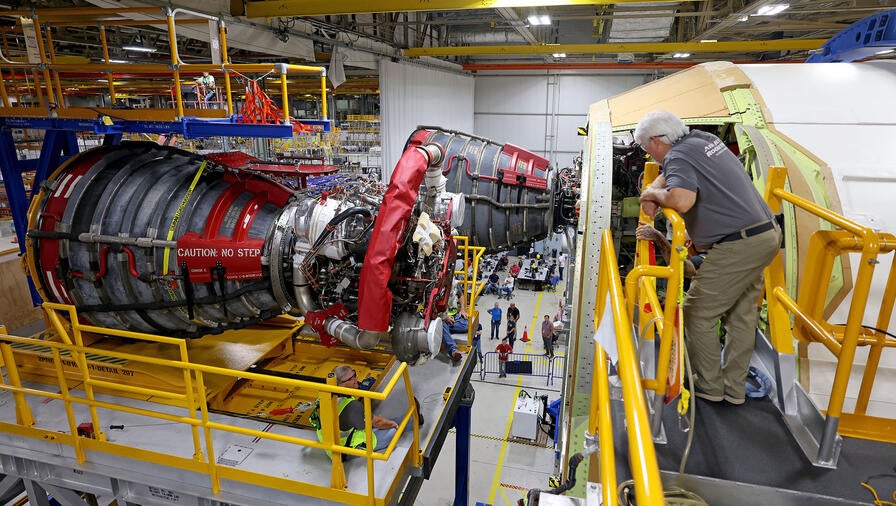
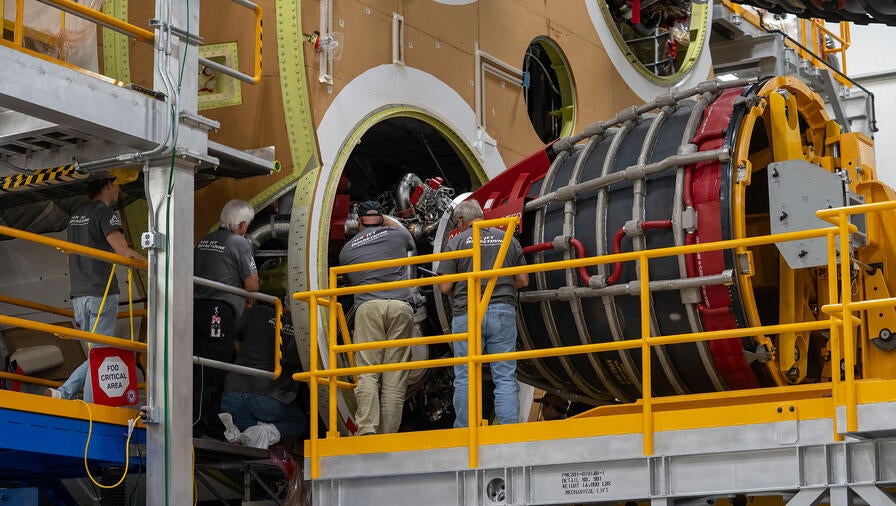
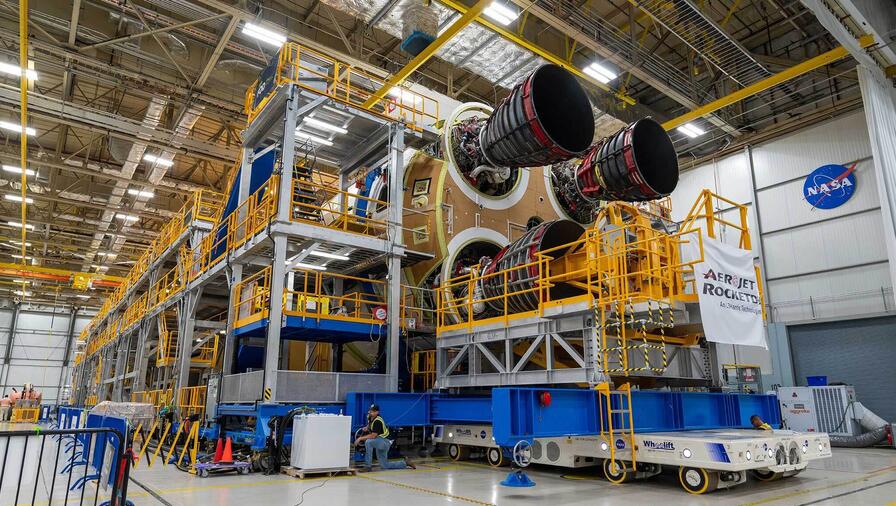
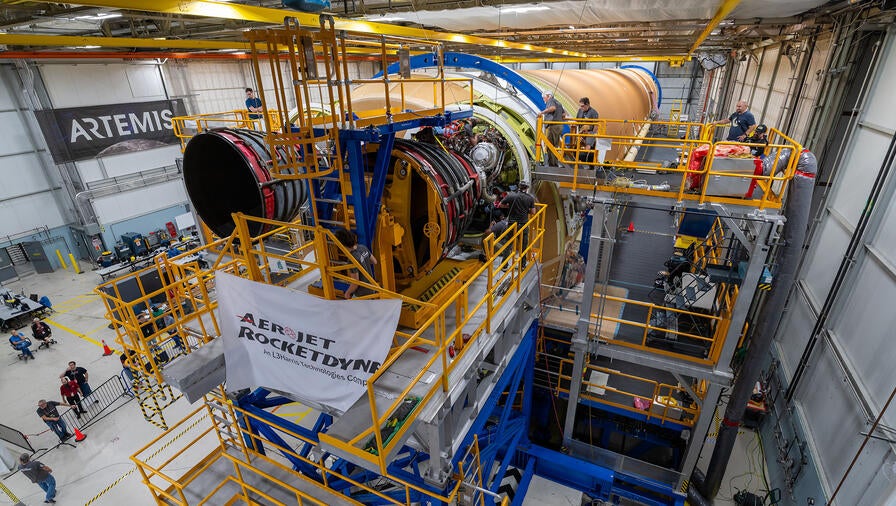
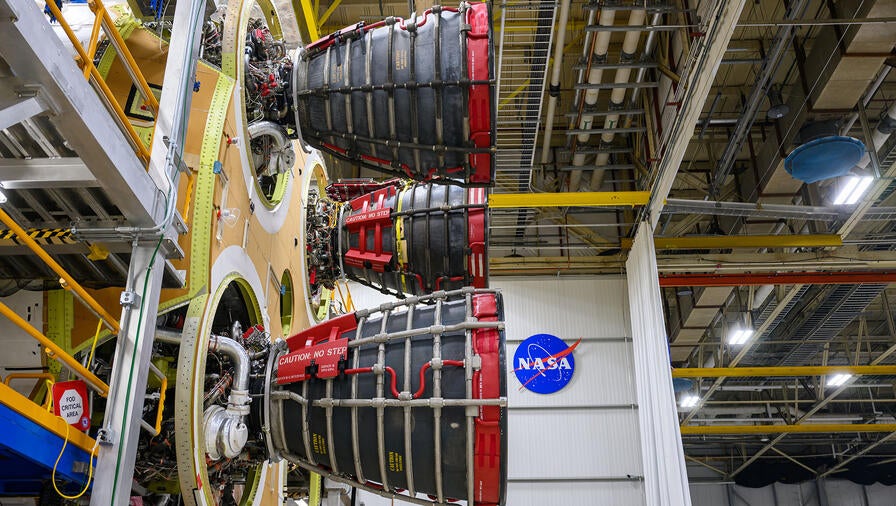
Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company, recently completed installation of all four RS-25 main engines on the core stage of NASA’s second Space Launch System (SLS) exploration rocket, binding them to a common destiny: launching humans beyond low Earth orbit for the first time in more than five decades.
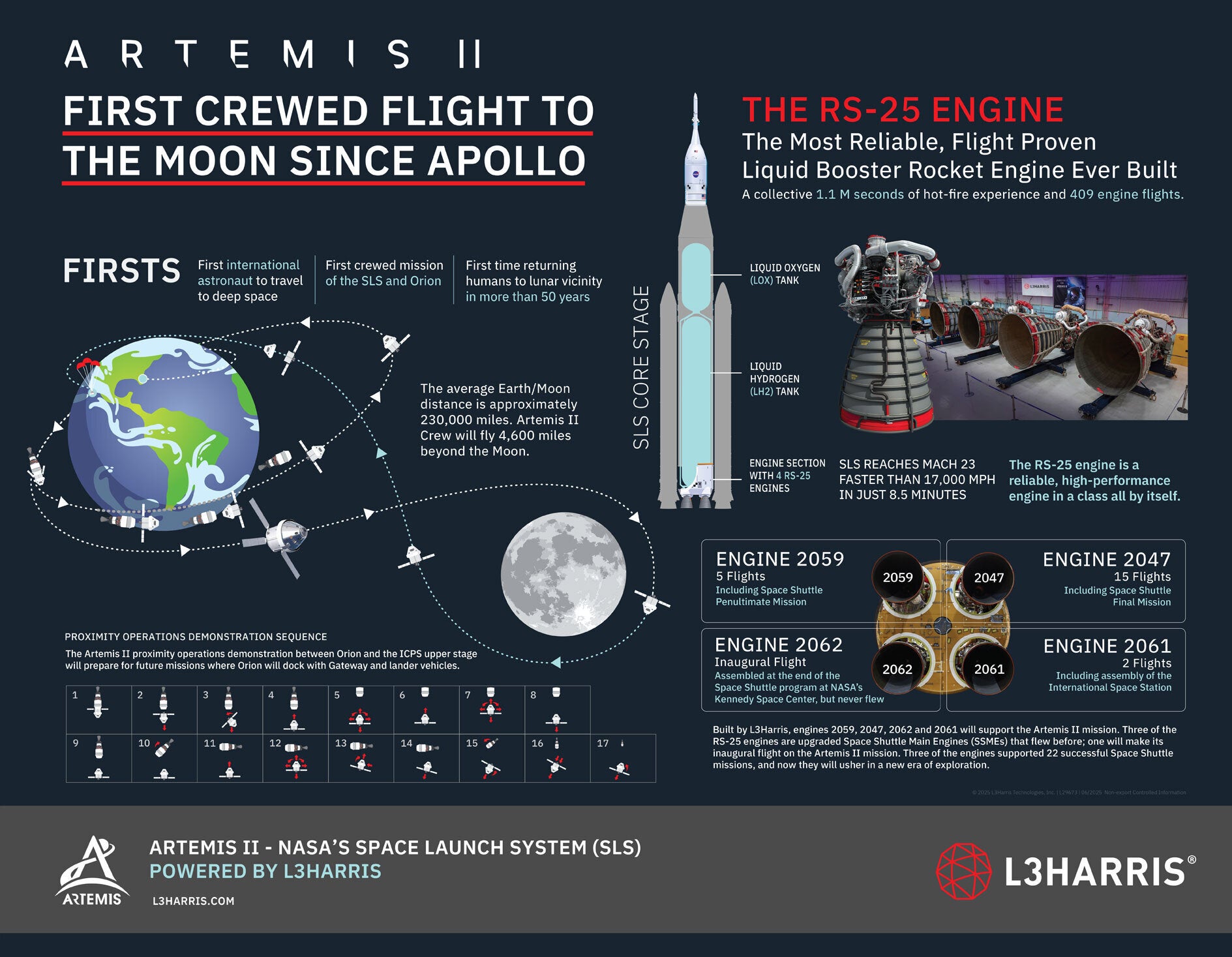
Three of the RS-25 engines are upgraded Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSMEs) that flew before; and one will make its inaugural flight on the Artemis II mission. Slated to launch in 2024, all four RS-25 engines will help send NASA’s Artemis II crew aboard the Orion spacecraft around the Moon, marking the first time a woman and a person of color has made this journey.
“The installation process for Artemis II went very smoothly because we were able to incorporate many lessons learned from the Artemis I mission,” said Bill Muddle, lead RS-25 field engineer at Aerojet Rocketdyne.
The RS-25 engines for the initial SLS rockets that will power the early Artemis missions were upgraded with new controllers and other features to enable deep space exploration. All four Artemis II engines have at least one component that flew aboard Space Shuttle Columbia during STS-1, the first shuttle mission. Engine 2047 flew on STS-135, the final shuttle mission, while engine 2059 flew on STS-134, the program’s penultimate flight and engine 2061 supported assembly of the International Space Station. Between them, engines 2047, 2059 and 2061 flew 22 space shuttle missions.
Engine number 2062 is unique among the 16 engines from the shuttle inventory, as it has never flown in space, although it does contain some components, such as high- and low-pressure pumps and valves that have. Aerojet Rocketdyne assembled the engine using main components that were built for the shuttle program but never had the chance to fly, including the nozzle and main combustion chamber.
“Engine 2062 has the distinction of being the last engine built for the shuttle program,” said Muddle. “It was test fired on the ground at NASA Stennis.”
Over the coming weeks, the SLS core stage for Artemis II will undergo a series of electronic, pneumatic and hydraulic tests to verify full integration before being shipped by NASA’s Pegasus barge to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in preparation for its launch.
Starting with its fifth mission, SLS will use brand new RS-25 engines that will cost 30% less than the engines produced for the shuttle program. Major components for these engines are already being built by Aerojet Rocketdyne using the latest manufacturing technologies and processes to achieve the targeted cost savings. Once produced, all RS-25 engines will be tested at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, prior to launch on an SLS flight.
“These new RS-25 engines will propel NASA and all of humanity to new heights, all thanks to the trail blazed by the legacy SSMEs,” added Muddle.