Overview
NOAA's GOES-R Advanced Baseline Imager
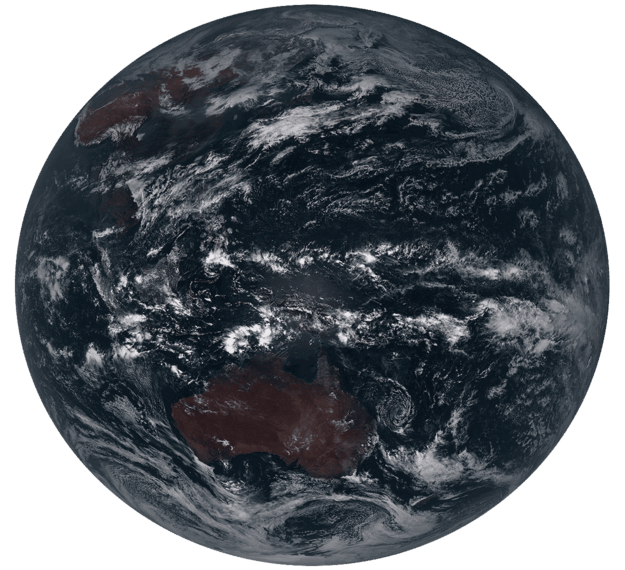
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s ABI instrument is the primary payload aboard the GOES-R satellite series, initially launched on 19 November 2016. It collects weather, climate, ocean, and environmental information in the Earth's western hemisphere. ABI views Earth with 16 spectral bands (compared to five on previous GOES system) and provides three times more spectral information, four times the spatial resolution, and more than five times faster coverage than the previous generation imager. The ABI is a mission-critical payload on the satellite, providing more than 65 percent of all mission data products currently defined. Now in geostationary orbit, joining its predecessor weather satellites, the GOES-T satellite was officially renamed to GOES-18.
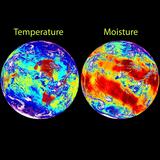
ABI monitors three times the number of atmospheric conditions than current geostationary imagers and will produce images that can discern objects as small as one-half a kilometer. It is also fast, updating data every 30 seconds while also creating a full-Earth image (CONUS) in only five minutes, and full disk image in ten minutes.
ABI can track a single storm, at full resolution, while simultaneously collecting continent-wide data and imagery. All these improvements add up to faster and more accurate forecasts, improved hazardous weather tracking, and increased capability to study and monitor climate change.
Advanced Himawari Imager
The first ABI-class imager launched, known as the Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI), was launched 7 October 2014 on the Himawari-8 satellite for the Japanese Meteorological Agency (JMA). AHI provides a number of improvements compared with current capabilities, including better forecasting, improved numerical weather prediction accuracy, and enhanced environmental monitoring. Environmental intelligence provided by AHI will give forecasters better data faster and at a higher resolution to provide advanced warning during dangerous weather, which is critical to saving lives and property. The first AHI became operational on 7 July 2015. JMA launched its second AHI instrument on board the Himawari-9 satellite on 2 November 2016.
The Himawari-8 and -9 geostationary satellites have replaced Japan's Multifunctional Transport Satellite (MTSAT) series. L3Harris imaging technology was also aboard the MTSAT-2 satellite.
Advanced Meteorological Imager
Launched in December 2018, the Korea Aerospace Research Institute's second geostationary satellite, the Geostationary Korea Multi-Purpose Satellite - 2A (GEO-KOMPSAT-2A), will carry the Advanced Meteorological Imager (AMI). The GEO-KOMPSAT-2A and a second satellite, GEO-KOMPSAT-2B, will replace to the Communication, Ocean and Meteorological Satellite (COMS-1) in its mission to observe the weather and ocean environment and strengthen the national capability to monitor the environment around the Korean Peninsula.